The docs are moving!
Find us at our new Help Center where we've combined our documentation and knowledgebase articles in one easy-to-search location.
We aren't updating the Developer Portal anymore, except for the Element Docs — all updates happen in the Help Center. We're retiring the Developer Portal as you know it in:
Element Builder Configuration and Parameters
Element configuration and parameters work together solve various scenarios presented by API providers. When you set up your element configuration, you define the information that you want to store with the element. The information can include data that you collect from the user when they authenticate an instance of an element. You can also store variables in the configuration that you can act on with parameters and hooks. You can also store information that you need to pass with each request to the API provider.
Parameters enable you to configure information that you need to send to an API provider with each request and how they expect to receive it. You can pass variables that you added to the configuration, information provided by the user, specific values, and more.
Reserved Configurations
Each parameter that you set up when defining the authentication information is available as an element configuration. The element configuration also includes the properties of the element: pagination information and base URL. The configuration Keys associated with the authorization and pagination parameters are reserved. You will receive an error if you try to create a configuration with a reserved configuration Key. The following table shows reserved configuration Keys.
| OAuth Keys | Basic Keys | Properties Keys | Events and Bulk | AWS Keys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oauth.basic.header | username | base.url | Any keys beginning bulk. | aws.api.key |
| oauth.user.refresh_time | password | pagination.type | Any keys beginning event. | aws.api.secret |
| oauth.user.refresh_token | pagination.max | event.notification.instance.finder | aws.region | |
| oauth.user.refresh_interval | pagination.page.startindex | event.vendor.type | expires | |
| oauth.user.token | event.poller.refresh_interval | expires_in | ||
| oauth.api.key | event.notification.enabled | |||
| oauth.scope | event.notification.callback.url | |||
| oauth.token.url | event.poller.configuration | |||
| oauth.api.secret | event.notification.subscription.id | |||
| oauth.authorization.url | event.metadata | |||
| oauth.token.refresh_url | event.helper.key | |||
| oauth.callback.url | ||||
| oauth.request.authorization.type | ||||
| oauth.request.url | ||||
| oauth.token.revoke_url | ||||
| oauth.user.token.secret |
Set Up Element Configuration
The element configuration is the storage place for any data that you need to operate on with parameters and hooks. For example, if the API provider requires something specific with each request, you can add that to the configuration and then define a parameter that passes the data with each request. You can expose the configuration to the user so that they can supply the information when they authenticate. Or, if it is not user specific information, you can store a default value in the configuration to act on later.
Before you set up configurations, review the Element Conventions so your element will align with others in the Elements Catalog.
To set up a configuration:
- Navigate to Configuration, and then click
 .
. - In Key you can choose to update the value automatically created from the configuration name or leave it. The configuration Key identifies the configuration property in the element configuration. You also use the configuration Key to refer to the configuration in parameters and hooks.
- Enter the name of the configuration. If you choose to show this on the UI, Cloud Elements will show the configuration name as you define it here.
- In Type select the type of configuration. Configurations can be text strings, boolean, or passwords.
- In Default enter any default value for the configuration. If shown on the UI, a user can overwrite the default value.
- In Description enter a brief description of the configuration. If the configuration appears in Cloud Elements, the description is available as hover help.
- To make the configuration a required part of authentication, switch Required on.
- Switch Hide UI to on to prevent the configuration from appearing on the UI when the user authenticates. By default, the configuration appears on the UI.
- Click Save.
Element Configuration Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | The visible name of the configuration as it appears in the Cloud Elements UI. | Y |
| Key | The internal unique identifier for the configuration. The configuration key value appears in the authentication JSON. You also refer to the configuration by configuration key in parameters and hooks. | Y |
| Type | The type of configuration, which can be any of the following: | Y |
| Text Area, Text Text 32, Text 64, Text 100, Text 128 — Identifies configurations that accept free text strings. | ||
| true/false and yes/no — Identifies configurations that accept boolean inputs. | ||
| password — Identifies configurations intended to collect passwords. Passwords are masked in Cloud Elements. | ||
| Required | Identifies whether the configuration is required. Switch on to force a user to provide data when authenticating. Configurations not required, but that show in Cloud Elements appear under Show Optional Fields. | Y |
| Hide on UI | Identifies whether the configuration appears in Cloud Elements. Switch on to show the configuration in Cloud Elements. The configuration appears to the user with the configuration name and the description as hover help text. | Y |
| Configuration Description | The description appears as hover help text. The text space available is limited, so write brief but useful descriptions. | Y |
| Default Value | The default value of the configuration. | N |
Set Up Element Parameters
Element parameters allow you to pass various properties with each request. You can create parameters that require user input or parameters that get their values from other sources. Use the element parameters to configure required query parameters, searches, pagination, ids, and required fields. You can configure most required and optional parameters for most APIs using parameters and configurations. Map parameters that you send as part of the request from Cloud Elements on the top row to parameters available to the resource at the API provider on the bottom row.
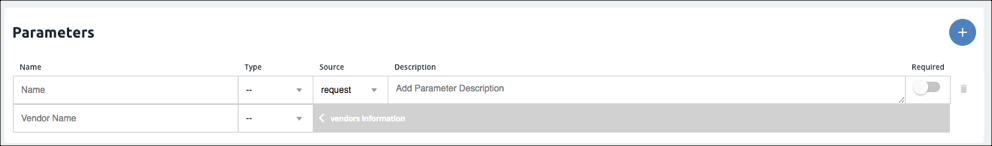
Before you set up parameters, review the Element Conventions so your element will align with others in the Elements Catalog. Each parameter includes information about how the parameter is used at Cloud Elements and how the API provider expects to receive the parameter.
To define a parameter :
- Navigate to Configuration, and then click
 .
. - Complete the top row of Cloud Elements parameter information:
- In Name enter the name of the parameter. The name appears in the API documentation and should match any existing values. For example, if you choose a type of "configuration", the name must match the configuration key it refers to. a type of "configuration", the name must match the configuration key it refers to.
- In Type select the source of the parameter. Refer to Cloud Elements Parameter Type in the Element Parameter Fields table.
- If you want to switch the standard workflow where the parameters in the top row are part of the request from Cloud Elements, and want the parameters on the top row to represent the response from the API provider, click Source, and then select Response.
- In Description enter a brief description of the parameter. If the parameter appears in the API documentation, this description also appears.
- Complete the bottom row of API provider parameter information:
- In Name enter the name of the API provider's name for the parameter to map to.
- In Type select select how the API provider receives the parameter. Refer to API Provider Parameter Type in the Element Parameter Fields table.
- Click Save.
Element Parameter Fields
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Elements Parameter Name | The parameter name acts as a key and provides values to the Parameter Types. | Required |
| Cloud Elements Parameter Type | The source of the parameter value on the Cloud Elements side. | Y |
| configuration — The value of the parameter is the value of the configuration identified by the configuration Key specified in the Parameter Name. The Parameter Name must match a configuration Key in the element configuration. | ||
| header — The value is the request header parameter that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| path — The value is the part of the request path that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| body — The value is the part of the request body that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| query — The value is the query parameter that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| form — The value is the value of the key that matches the Parameter Name in the x-www-form-urlencoded body of a request. If a file, then use "file" as the Parameter Name. | ||
| multipart — The value is the value of the key that matches the Parameter Name in the x-www-form-urlencoded body of a request. If a file, then use "file" as the Parameter Name. | ||
| value — The value is the Parameter Name. | ||
| bodyField — The value is the value of the field in a request body that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| prevBody - Cloud Elements parameter type only. If chaining requests, the value is the part of the request body of the previous request in the chain that matches the Parameter Name. | ||
| prevBodyField - Cloud Elements parameter type only. If chaining requests, the value is the field in the request body of the previous request in the chain that matches the Parameter Name | ||
| Source | Identifies the side that represents the source, or left side of the parameter. The default request identifies Cloud Elements as the source. If you choose response, you effectively flip the Cloud Elements and API provider sides. | Y |
| Description | A free text area to describe the parameter. | N |
| API Provider Parameter Name | The parameter at the API provider that equals the parameter that you are defining. | Required |
| API Provider Parameter Type | The destination of the parameter value on the API provider side.: | Y |
| configuration — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as part of the configuration. | ||
| header — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value in the header. | ||
| path — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value in the path. | ||
| body — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value in the body. | ||
| query — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as a query parameter. | ||
| form — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as part of the x-www-form-urlencoded body of a request. | ||
| multipart — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as part of the x-www-form-urlencoded body of a request. | ||
| value — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as a value. | ||
| bodyField — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as a body field. | ||
| bodyToken — Requests to the API provider pass the parameter value as a body token. | ||
| no-op — Indicates that the API provider does not need to operate on the parameter. Use no-op if you use the parameter in hooks. |
Delete Configurations and Parameters
You can delete an element configuration or parameter. When you delete the configuration or parameter, Cloud Elements does not check for references in hooks or to other element configurations.
To delete a configuration or parameter, click Delete  .
.
Continue to the next step, Custom Hooks.